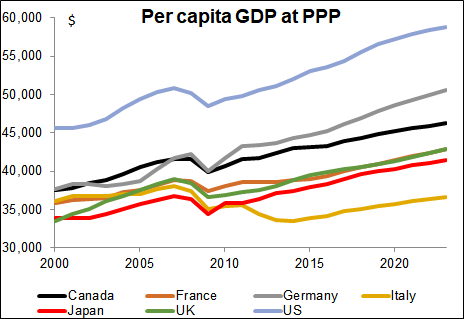
Introduction
Japan, once heralded as an economic powerhouse, is currently experiencing a notable decline in its Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This downturn is attributed to a confluence of factors, including demographic challenges, stagnant wages, and global economic conditions. Understanding these elements is crucial for grasping the broader implications for Japan’s economy and its position in the global market.
Contents
Historical Context
Japan’s economic trajectory has been tumultuous since the bursting of its asset bubble in the early 1990s. The country enjoyed rapid growth post-World War II, becoming the second-largest economy globally by the 1980s. However, since the 1990s, Japan has faced persistent stagnation, often referred to as the “Lost Decades.” This period has been characterized by low growth rates, deflationary pressures, and an aging population.
Key Factors Contributing to GDP Decline
1. Demographic Challenges
Japan’s population is both shrinking and aging. As of 2023, the country has one of the highest proportions of elderly citizens globally. This demographic shift leads to:
- Reduced Labor Force: A declining working-age population constrains economic output.
- Increased Dependency Ratio: More retirees relative to workers increases the burden on social security systems and reduces disposable income.
2. Stagnant Wages and Consumption
Despite low unemployment rates, wages in Japan have not kept pace with inflation. Key points include:
- Real Wage Decline: In 2023, real wages fell by 2.5%, marking two consecutive years of decline.
- Consumer Reluctance: Stagnating wages have led to decreased household spending, contributing to a sluggish domestic demand that accounts for over half of Japan’s GDP.
3. Global Economic Conditions
Japan’s economy is heavily reliant on exports. Recent global trends have negatively impacted this sector:
- Weak External Demand: Slowing growth in major markets like China affects Japanese exports.
- Trade Deficits: Japan has faced widening trade deficits due to a decline in exports coupled with rising import costs.
4. Policy Mismanagement
Historical policy decisions have also played a role in Japan’s economic malaise:
- Consumption Tax Hikes: Increases in consumption tax have stifled consumer spending during recovery periods.
- Lack of Structural Reforms: The government has been criticized for failing to implement necessary reforms that could stimulate growth and productivity.
5. Technological Lag
Japan’s industrial sector has struggled to adapt to new technologies and market demands:
- Slow Adoption of Electric Vehicles: The automotive industry, once a strength, faces challenges from global shifts towards electric vehicles.
- Investment Abroad: Japanese companies are increasingly investing overseas rather than in their domestic markets, further weakening local economic activity.
Economic Indicators
The following table summarizes key economic indicators relevant to Japan’s GDP situation:
| Indicator | Value (2023) |
|---|---|
| Nominal GDP | $4.21 trillion |
| Real GDP Growth Rate | -0.4% (Q4 2023) |
| Unemployment Rate | ~2.5% |
| Real Wage Change | -2.5% |
| Trade Deficit | $13.6 billion |
For more detailed statistics and insights on Japan’s economy, refer to this source.
Future Outlook
The outlook for Japan’s economy remains cautious. Analysts predict continued sluggish growth due to:
- Persistent Inflation: Rising prices without corresponding wage increases will likely suppress consumer spending.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and trade issues may further hinder export performance.
Conclusion
Japan’s declining GDP is a multifaceted issue rooted in demographic challenges, stagnant wages, global economic shifts, policy mismanagement, and technological lag. Addressing these problems will require comprehensive reforms and innovative solutions to revitalize the economy.
FAQ Section
1. Why is Japan’s GDP declining?
Japan’s GDP is declining due to an aging population, stagnant wages leading to reduced consumer spending, weak external demand for exports, and historical policy mismanagement.
2. What role does demographic change play?
The aging population reduces the labor force and increases the dependency ratio, placing additional strain on social services and limiting economic growth.
3. How do global economic conditions affect Japan?
Slowing growth in key markets like China impacts Japanese exports significantly, contributing to trade deficits and overall economic decline.
4. What policies could help improve Japan’s economy?
Implementing structural reforms aimed at increasing productivity, enhancing labor market participation, and fostering innovation could help stimulate economic growth.
5. Is there hope for recovery?
While challenges remain significant, targeted reforms and strategic investments could potentially lead to gradual recovery if implemented effectively.This comprehensive overview highlights the complexities surrounding Japan’s declining GDP while providing insights into potential pathways for recovery.


