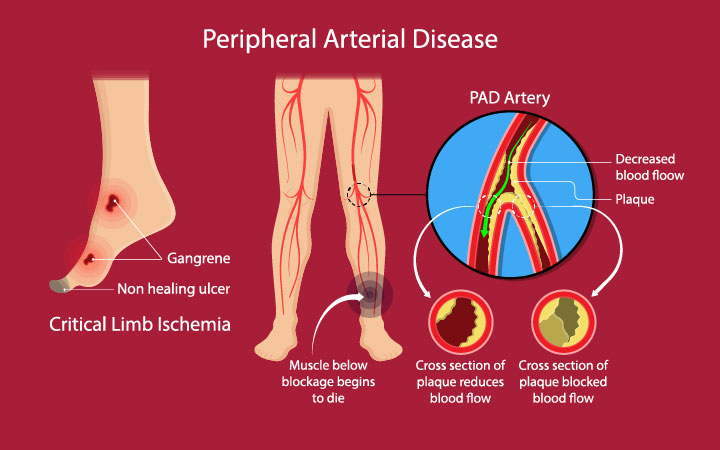
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a prevalent circulatory disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. PAD occurs when there is a narrowing or blockage of the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, most commonly the legs. This condition often leads to pain, limited mobility, and an increased risk of complications such as ulcers and infections. Over the years, significant advancements in pad vascular surgery have revolutionized treatment options, enabling medical professionals to restore blood flow, alleviate symptoms, and ultimately improve the quality of life for those affected by this debilitating condition.
Contents
Endovascular Techniques: A Less Invasive Approach
Traditionally, open surgical procedures were the primary method for treating PAD. However, recent advancements in endovascular techniques have transformed the landscape of PAD treatment. Endovascular procedures involve accessing the affected artery through a small incision, often in the groin area, and using specialized tools to navigate the vascular system to the site of the blockage. This approach offers several benefits, including reduced trauma, shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and lower risks of complications.
Angioplasty and Stenting: Restoring Blood Flow
Angioplasty, a cornerstone of endovascular techniques, involves inflating a balloon within the narrowed artery to widen it and restore blood flow. This procedure has become even more effective with the introduction of stenting, where a mesh-like device is inserted to keep the artery open after angioplasty. Drug-eluting stents, coated with medications that inhibit tissue growth, have further improved the long-term success of this technique by minimizing the risk of re-narrowing, or restenosis.
Atherectomy: Removing Plaque Buildup
Atherectomy is another breakthrough in PAD vascular surgery, particularly useful when dealing with heavily calcified blockages. This technique involves using a specialized catheter equipped with cutting or grinding mechanisms to remove plaque buildup from the arterial walls. Atherectomy not only improves blood flow but also enhances the effectiveness of other procedures, such as angioplasty and stenting.
Minimally Invasive Bypass Surgery: A Game Changer
While traditional bypass surgery involves creating a detour around the blocked artery using a graft, advancements in minimally invasive bypass procedures have brought significant improvements to this technique. These minimally invasive approaches require smaller incisions, resulting in reduced pain, faster recovery, and improved cosmetic outcomes. Robotic-assisted techniques further enhance precision and allow surgeons to perform intricate procedures with greater accuracy.
Advancements in medical imaging and navigation technologies have greatly contributed to the success of modern PAD vascular surgery. High-resolution imaging, such as angiography and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), enables surgeons to visualize the arterial system in real-time, guiding their actions during procedures. Additionally, the integration of 3D mapping and navigation systems provides detailed insights into the vascular anatomy, facilitating the planning and execution of complex interventions.
Conclusion
The field of PAD vascular surgery has undergone remarkable advancements, ushering in a new era of innovative and minimally invasive treatments. These advancements, including endovascular techniques, angioplasty with stenting, atherectomy, and minimally invasive bypass surgery, have collectively transformed the landscape of PAD management. By restoring blood flow, reducing symptoms, and improving patients’ overall quality of life, these advancements underscore the continuous commitment of the medical community to enhance patient care and well-being. As research and technology continue to evolve, the future holds even greater promise for individuals affected by PAD, offering them hope for a healthier and more active life.